By using our website, you agree to the use of cookies as described in our Cookie Policy
Blog
First Quarter 2019 Key Takeaways
After posting their worst December since 1931, U.S. stocks surged to their best January since 1987, followed by further gains in February and March. Once again, the markets surprised the consensus and demonstrated the folly of trying to predict short‐term performance. Investors who bailed out of stocks during the year‐end selloff experienced severe whiplash as the market rallied. Larger‐cap U.S. stocks gained 13.6% for the quarter, placing it in the top decile of quarterly market returns since 1950. As a reminder, last year’s fourth quarter 14% drop was a bottom‐decile dweller.
Foreign stocks also rebounded sharply in the first quarter. Developed international markets gained 10.6% and European stocks were up 10.9%. Emerging‐market (EM) stocks rose 11.8%, after holding up much better than U.S. stocks on the downside in the fourth quarter of 2018.
Fixed‐income markets were also strong: High‐yield bonds gained 7.4%, floating‐rate loans were up 4%, and investment‐grade bonds rose 2.9%. The 10‐year Treasury yield fell to 2.39% during March, its lowest level since December 2017. Our tactical positions in actively managed flexible income funds also generated strong returns. They outperformed the benchmark core bond index as a group this quarter. These strategies are positioned to continue delivering strong relative performance given their low duration and higher yields.
Turning to alternative investments, our lower‐risk alternative strategy funds generated positive returns that were better than core bonds but well below the soaring stock market. This is consistent with our performance expectations given their lower‐risk and more‐defensive positioning. Some of the gains simply arose from equity beta, but other gains were procured from low correlation funds such as merger arbitrage and event driven strategies. Despite a choppy past few months, managed futures also rebounded in March to finish at level ground for the quarter.
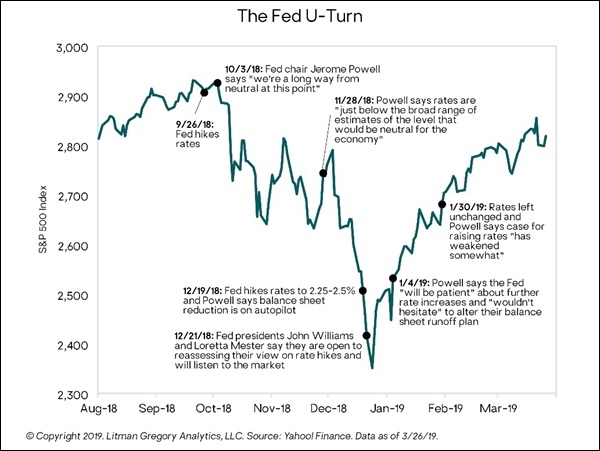
The market rebound was predominately due to a U‐turn in Federal Reserve monetary policy. After hiking interest rates four times in 2018, Fed officials suddenly reversed course. They emphasized they would be “patient” and pause any further rate increases. Admittedly, there were other positives for the markets as well: The federal government shutdown ended in late January, signals from the U.S.‐China trade talks turned more positive, and the likelihood of a “hard Brexit” seemed to wane. In the end though, the Fed’s 180 on rates gave the equity market the green light to move higher.
It certainly feels better to see strongly positive portfolio performance this quarter compared to the losses in the fourth quarter of 2018. However, just as we wouldn’t extrapolate last year’s losses when looking out over the coming years, it’s equally important to temper our expectations on the upside after this quarter’s strong rebound. This rebound in risk asset prices returns the market to levels seen in the fall of 2018.
If monetary and fiscal stimulus around the globe extend the cycle for another few years, we have exposure to a wide range of investments that will particularly benefit. These include global equities, with an emphasis on developed international, European, and emerging‐market stocks; flexible income funds; and (to a lesser degree) floating‐rate loan funds.
On the other hand, if a recessionary bear market strikes, our holdings in core bonds, lower‐risk hybrid and alternative strategies, and trend‐following managed futures funds should perform well on a relative basis. And we would then be in position to tactically add back to riskier asset classes, such as U.S. stocks, at lower prices and higher prospective medium‐term returns.
First Quarter 2019 Investment Letter
Market Recap
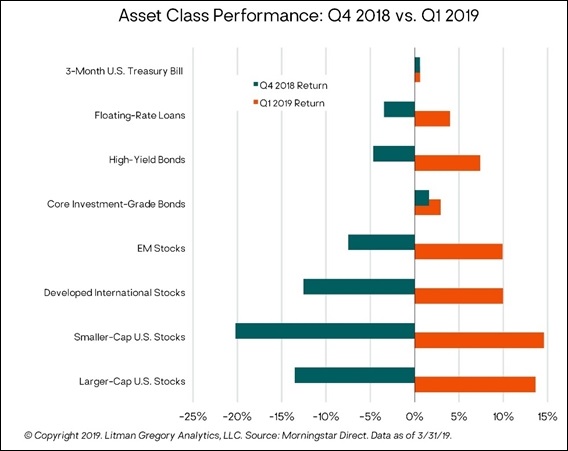 On the heels of their worst December since 1931, U.S. stocks opened 2019 by scoring their best quarter since the financial crisis. Larger‐cap U.S. stocks gained 13.6%, placing the S&P 500 Index’s performance in the top decile of quarterly market returns since 1950. Not to be left behind, foreign equities, which were by far the most battered coming out of 2018, generated double‐digit returns: emerging‐market stocks rose 11.8%, while developed international stocks gained 10.6% and European equities gained 10.9%.
On the heels of their worst December since 1931, U.S. stocks opened 2019 by scoring their best quarter since the financial crisis. Larger‐cap U.S. stocks gained 13.6%, placing the S&P 500 Index’s performance in the top decile of quarterly market returns since 1950. Not to be left behind, foreign equities, which were by far the most battered coming out of 2018, generated double‐digit returns: emerging‐market stocks rose 11.8%, while developed international stocks gained 10.6% and European equities gained 10.9%.
Fixed‐income markets were also strongly positive. High‐yield bonds earned 7.4% in the first quarter, floating‐rate loans were up 4%, and the core investment‐grade bond index returned 2.9%. The 10‐year Treasury yield fell to 2.39% during March, its lowest level since December 2017, after peaking at 3.24% late last year.
The market rebound was predominately due to a reversal in Fed monetary policy. After hiking interest rates four times in 2018, including at their mid‐December meeting, and indicating further tightening would occur in 2019, Fed officials suddenly reversed course. They emphasized they would be “patient” and pause any further rate increases. And—presto!—stocks are back at their highs of late last summer.
Admittedly, there were other positives for the markets as well: The federal government shutdown, which had started to weigh on sentiment, ended in late January; signals from the U.S.‐China trade talks turned more positive; and the likelihood of a “hard Brexit” also seemed to wane. But, in the end, thank the Fed for this bounce.
Portfolio Attribution
Our portfolios generated strong performance for the first quarter, largely driven by their exposure to U.S., international, and emerging‐market stocks. Unlike 2018, all major equity asset classes moved in tandem. The weight of the trade wars seemed to dissipate and foreign stocks captured a good portion of U.S. stock returns.
Our tactical positions in actively managed flexible income and floating‐rate loan funds also generated strong returns and outperformed the benchmark core bond index in aggregate. Despite interest rates backing up in the first quarter, credit sensitive strategies performed well as the equity markets rebounded.
Our allocation to liquid alternative funds also had a strong first quarter, in part buoyed by the sharp recovery in equities. Not surprisingly, strategies such as long‐short equity and tactical allocation led the way, as both were positioned to reap the benefits of a rising equities market. Merger arbitrage and event driven funds continued their steady growth, and managed futures posted a strong March, which helped it recover from trend reversals in
January and February. Overall, the returns to our alternatives met our performance expectations—though their lower risk profile meant they would be unable to keep pace with equities, they nonetheless outperformed core
bonds.
Given the high valuations for US equities and the strong first quarter, we have decided to “lock in” the gains that some liquid alternatives made through March, and will now increasingly emphasize in our alternatives sleeve those funds that have little correlation to the equities market. In general, this will entail a shift away from categories such as long‐short equity, and a relatively larger share of assets in categories such as merger arbitrage. Ultimately, while we will evaluate each of our liquid alternatives on a strategy by strategy basis, we believe that the maturity of this extended bull market, as well as the likelihood of slowing US and global growth, dictates that we should adopt a somewhat more defensive approach to markets within this basket.
Market Outlook
The obvious question after experiencing such a rebound is, what’s next? It’s easy to be enamored with the U.S. equity market, especially when the Fed is playing its cards face up. However, the reality is the market rebound was due more to improving investor sentiment and risk appetite—caused largely by the shift in Fed monetary policy—than any meaningful improvements in underlying economic or business fundamentals.
From our vantage point, looking out over our longer‐term investment horizon, seemingly little has changed after the roller coaster ride of the last six months. The first quarter of 2019 was certainly a nice respite from the losses of 2018, but we remain prepared for renewed market choppiness as the economic cycle gets later and later (and closer and closer to the inevitable downturn).
While the U.S. economy is still arguably the strongest market, growth expectations have been coming down. At its Federal Open Market Committee meeting on March 20, the Fed downgraded its median GDP growth estimate to just 2.1% for 2019 and 1.9% for 2020, citing the effects of economic slowdowns in China and Europe, fading stimulus from the 2017 Trump tax cuts, and ongoing uncertainty around Brexit and trade policy.
U.S. corporate earnings growth expectations also continue to decline. Consensus earnings‐per‐share growth estimates for the S&P 500 have dropped from 12% (as of 12/31/18) to just 4.1% as of mid‐March. Even with the Fed now on hold, earnings growth will need to improve for stocks to appreciate meaningfully from current levels, given their sharp rebound in the first quarter and higher valuations. Our annualized return expectations for U.S. stocks are in the low to midsingle‐ digit range over the next five years.
 On the other hand, there are a number of short‐term scenarios that could see further equity gains, in particular in foreign markets. The Chinese government is once again trying to boost their economy via fiscal and monetary policy (including tax cuts, lower interest rates, and expanded bank lending). A revival in Chinese growth would have positive ripple effects across the global economy. It would benefit other emerging markets and Europe in particular, asChina is a major importer of their goods. This foreign stimulus, combined with the Fed’s policy U‐turn, may enable equity markets to extend their positive run for another few years. This outcome would almost certainly benefit our portfolio positions in developed international and emerging markets, among other riskier assets.
On the other hand, there are a number of short‐term scenarios that could see further equity gains, in particular in foreign markets. The Chinese government is once again trying to boost their economy via fiscal and monetary policy (including tax cuts, lower interest rates, and expanded bank lending). A revival in Chinese growth would have positive ripple effects across the global economy. It would benefit other emerging markets and Europe in particular, asChina is a major importer of their goods. This foreign stimulus, combined with the Fed’s policy U‐turn, may enable equity markets to extend their positive run for another few years. This outcome would almost certainly benefit our portfolio positions in developed international and emerging markets, among other riskier assets.
While we’d prefer to see global growth rebound with continued strong performance, we believe it is wise to be prepared (both mentally and financially) for shorter‐term downside and negative market surprises. If and when a recessionary bear market strikes, we will look to our holdings in core bonds as well as our higher‐yielding multisector strategies and lower risk alternative strategies to provide ballast to our portfolios and limit the impact of equity declines.
Any prolonged downturn will also likely present us with opportunities to tactically increase our exposure to riskier asset classes, such as U.S. stocks, at lower prices and higher prospective returns compared to what is available today.
As always, we appreciate your trust and confidence in our investment discipline, and we work hard every day to continue to earn it.
- JMS Team
JMS Capital Group Wealth Services LLC
417 Thorn Street, Suite 300 | Sewickley, PA | 15143 | 412‐415‐1177 | jmscapitalgroup.com
An SEC‐registered investment advisor.
This material is not intended as an offer or solicitation for the purchase or sale of any financial instrument or investment strategy. This material has been prepared for informational purposes only, and is not intended to provide, and should not be relied on for, accounting, legal or tax advice. Any references to future returns are not promises - or even estimates - of actual returns a client portfolio may achieve. Any forecasts contained herein are for illustrative purposes only and are not to be relied upon as advice or interpreted as a recommendation for a specific investment. Past performance is not a guarantee of future results.
With the exception of historical matters, the items discussed are forward‐looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from projected results. We have based these projections on our current expectations and assumptions about current and future events ‐ as of the time of this writing. While we consider these expectations and assumptions to be reasonable, they are inherently subject to significant business, economic, competitive, regulatory and other risks, contingencies and uncertainties, most of which are difficult to predict and many of which are beyond our control. There can be no assurances that any returns presented will be achieved.
‹ Back








